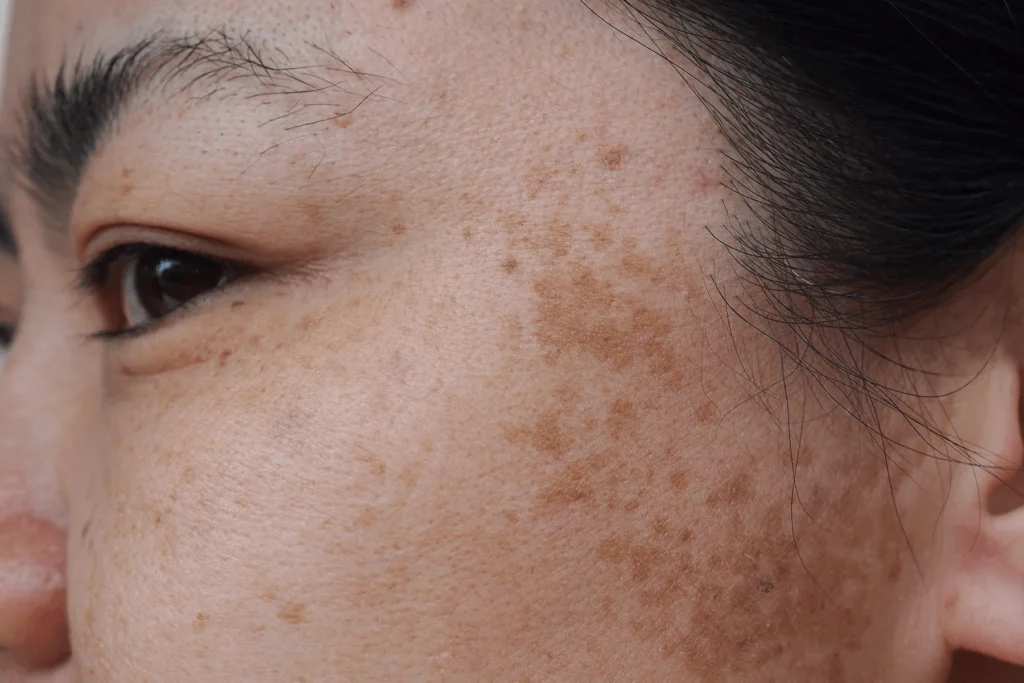
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches, typically on the face. It’s most often found on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip, though it can also appear on other sun-exposed areas of the body. While melasma is not harmful, it can be distressing due to its cosmetic appearance.
What Causes Melasma?
The exact cause of melasma isn’t fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute:
- Sun Exposure: UV rays from the sun stimulate melanocytes (pigment-producing cells), leading to the overproduction of melanin and the formation of dark patches.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy, are a major trigger. This is why melasma is sometimes called “the mask of pregnancy.”
- Genetics: A family history of melasma can increase your likelihood of developing it.
- Skincare Products: Certain products that irritate the skin can make melasma worse.
- Heat Exposure: Besides UV light, high temperatures can also worsen melasma.
Treatment Options for Melasma
While melasma can be challenging to treat, there are several options that may help lighten the pigmentation:
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, tretinoin, or corticosteroids are often used to reduce pigmentation. Over-the-counter optio
- ns with ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, or kojic acid can also help.
- Chemical Peels: Superficial chemical peels can help exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of dark patches.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers, such as Q-switched Ndor fractional lasers, can target pigmentation without damaging surrounding skin. However, not all lasers are suitable for melasma, so it’s important to consult a dermatologist who specializes in pigmentary disorders.
- Microneedling: Combined with topical treatments, microneedling can enhance the penetration of lightening agents and help improve melasma.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, oral medications like tranexamic acid have been prescribed to manage melasma, especially when it is resistant to topical treatments.
Preventing Melasma
Prevention is key to managing melasma, especially since it can recur even after successful treatment. Here are some tips:
- Sunscreen: Daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 is essential. Physical sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are often preferred as they offer better protection for sensitive skin.
- Sun Protection Habits: In addition to sunscreen, wearing hats, sunglasses, and avoiding direct sunlight, especially during peak hours, can help prevent melasma from worsening.
- Avoid Heat and UV Exposure: Limit exposure to not just the sun but also heat from other sources, such as saunas and hot environments.
- Skincare Routine: Opt for gentle, non-irritating skincare products. Avoid harsh scrubs or exfoliants that can inflame the skin and trigger melasma.
Living with Melasma
Dealing with melasma can be frustrating, but with proper care, many people see improvement. It’s important to approach treatment under the guidance of a dermatologist, as aggressive treatments can sometimes make the condition worse. The key to managing melasma is patience and consistency, particularly with sun protection and skincare.
If you’re struggling with melasma, consulting with a dermatologist can help tailor a treatment plan that’s right for you. With the right approach, you can achieve a more even complexion and take control of your skin’s health.
Remember, even celebrities deal with skin conditions like melasma, and the right treatments can make a world of difference!